What's Next
- Dimis Real Estate Hellas
- Real Estate Directory
- Histone Acetylation Mechanism
- Avahi Wooly Lemurs
- Lesvos Hotels
- What Lawyer to Choose
- Is Wikipedia Reliable
- Logic and Logical Thinking
- Style Tips and Style Advices
- Shopping Bags
- Real Estate
- Reviews of JigSaw Puzzles & Accessories
- SEO Services
- PlayFish Cheats
Actinomyces
Historically speaking the first written appearance of Actinomyces was made in 1877 when pathologist Otto Bollinger described their presence in cattle. Shortly after that James Israel discovered another specie of actinomyces or actinomycetes that are living in humans and in his honour these actinomyces have name actinomyces israelii.
As the years passed in 1890 Eugen Bostroem managed to isolate the causative organism from the grain, grass and soil, but that discovery led to a general misconception that actinomycosis would affect all individuals who chewed grass or straw. Today we know following things:
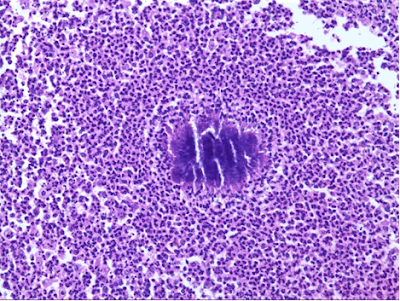
Actinomyces are an anaerobic or facultatively anaerobic filamentous gram-positive bacteria that is found in normal commensal in the mouth and throat. Their name comes from two Greek words AKTIS- ray and MYKES-fungus.The deffinition itself describes various description of actinomyces as following: Anaerobic organism represents any organism that doesn't require oxygen for its growth and in the presence of oxygen it may even die, while facultative anaerobic organism is usualy a bacteria that creates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is one of the most used enzyms or catalists or it can turn to the process of fermentation if it is exposed to the oxygen.Gram positive bacteria are those that according to Gram staining are dark blue or violet in colour. If bacteria is Gram negative it will not be able to retain the violet strain of crystal.
There are 19 species of actinomyces, but those that may cause disease on human are Actinomyces israelli and they are the cause of disease named Actinomycosis that will be more words about later. Most species are representatives of serologic groups with subtypes. Classification is based on analysis of DNA and RNA, structures of cell and walls, metabolic end products, serology and biochemical reactions.
Disease is limited to periodontal area of activity. There is one difference between actinomyces and other bacteria and that is that actinomyces don't form endospores and they form branched networks of hyphae that looks like fungus while other bacteria are in a shape of rod and they don't make branched networks. In fungi hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth and their collective name is mycelium.
Actinomyces are also very important in ecology of soil and the numerous enzymes that they produce helps a lot in degrading organic materials like lignin and chitin. Lingin(lingen) is a very compley chemical compound and mostly it is derivated from wood and it is an integral part of secondary cell walls of plants and some species of algae while Chitin is a long chain polymer of N-acetylglycosamine and it is also a derivative of glucose and it is found in many places trough the natural world (the cocoon of hard insects is built of chitin).
Some species are responsible for the smell of top soil which is noticeable after the rain and that smell appears because of geosmin that is the matery that they contain inside.
Many of the actinomyces are opportunistic source of disease and particularly in oral cavity.In rare cases actinomyces can cause actinomycosis that is characterised by the formation of abscesses in gastrointestinal tract, lungs and mouth.
Good oral hygiene may help in prevention of actinomycosis. Actinomycosis is treated with antibiotics and surgical drainage of lesions. In all Actinomyces infections penicillin is the drug of choice.

Davis's Drug Guide for Nurses, with Resource Kit CD-ROM
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition

Davis's Drug Guide for Nurses, with Resource Kit CD-ROM
Kaplan Medical USMLE Master the Boards Step 3 (Kaplan USMLE)
Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2009: Classic Shirt-Pocket Edition, Revised and Updated
First Aid for the USMLE Step 2 CK, Seventh Edition (First Aid USMLE)
First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2009: A Student to Student Guide (First Aid USMLE)
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition
As the years passed in 1890 Eugen Bostroem managed to isolate the causative organism from the grain, grass and soil, but that discovery led to a general misconception that actinomycosis would affect all individuals who chewed grass or straw. Today we know following things:
Actinomyces are an anaerobic or facultatively anaerobic filamentous gram-positive bacteria that is found in normal commensal in the mouth and throat. Their name comes from two Greek words AKTIS- ray and MYKES-fungus.The deffinition itself describes various description of actinomyces as following: Anaerobic organism represents any organism that doesn't require oxygen for its growth and in the presence of oxygen it may even die, while facultative anaerobic organism is usualy a bacteria that creates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is one of the most used enzyms or catalists or it can turn to the process of fermentation if it is exposed to the oxygen.Gram positive bacteria are those that according to Gram staining are dark blue or violet in colour. If bacteria is Gram negative it will not be able to retain the violet strain of crystal.
There are 19 species of actinomyces, but those that may cause disease on human are Actinomyces israelli and they are the cause of disease named Actinomycosis that will be more words about later. Most species are representatives of serologic groups with subtypes. Classification is based on analysis of DNA and RNA, structures of cell and walls, metabolic end products, serology and biochemical reactions.
Disease is limited to periodontal area of activity. There is one difference between actinomyces and other bacteria and that is that actinomyces don't form endospores and they form branched networks of hyphae that looks like fungus while other bacteria are in a shape of rod and they don't make branched networks. In fungi hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth and their collective name is mycelium.
Actinomyces are also very important in ecology of soil and the numerous enzymes that they produce helps a lot in degrading organic materials like lignin and chitin. Lingin(lingen) is a very compley chemical compound and mostly it is derivated from wood and it is an integral part of secondary cell walls of plants and some species of algae while Chitin is a long chain polymer of N-acetylglycosamine and it is also a derivative of glucose and it is found in many places trough the natural world (the cocoon of hard insects is built of chitin).
Some species are responsible for the smell of top soil which is noticeable after the rain and that smell appears because of geosmin that is the matery that they contain inside.
Many of the actinomyces are opportunistic source of disease and particularly in oral cavity.In rare cases actinomyces can cause actinomycosis that is characterised by the formation of abscesses in gastrointestinal tract, lungs and mouth.
Good oral hygiene may help in prevention of actinomycosis. Actinomycosis is treated with antibiotics and surgical drainage of lesions. In all Actinomyces infections penicillin is the drug of choice.
Resources
Books
Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (Pocket Notebook Series)Davis's Drug Guide for Nurses, with Resource Kit CD-ROM
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition
Resources
Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (Pocket Notebook Series)Davis's Drug Guide for Nurses, with Resource Kit CD-ROM
Kaplan Medical USMLE Master the Boards Step 3 (Kaplan USMLE)
Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2009: Classic Shirt-Pocket Edition, Revised and Updated
First Aid for the USMLE Step 2 CK, Seventh Edition (First Aid USMLE)
First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2009: A Student to Student Guide (First Aid USMLE)
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)